How to Calculate Treasury Stock Reissuances
How to Calculate Treasury Stock Reissuances
Dividends and Retained Earnings
Retained earnings is related to net income since it’s the net income amount saved by a company over time. When these companies suffer losses, the amounts are subtracted from the retained earnings carried from previous years.
However, because retained earnings are collected from when corporations are started, having negative balances can lead to serious problems such as bankruptcy. Instead, the corporation likely used the cash to acquire additional assets in order to generate additional earnings for its stockholders. In some cases, the corporation will use the cash from the retained earnings to reduce its liabilities. As a result, it is difficult to identify exactly where the retained earnings are presently.
For example, if Company A earns 25 cents a share in 2002 and $1.35 a share in 2012, then per-share earnings rose by $1.10. Of the $7.50, Company A paid out $2 in dividends, and therefore bookkeeping had a retained earnings of $5.50 a share. Since the company’s earnings per share in 2012 is $1.35, we know the $5.50 in retained earnings produced $1.10 in additional income for 2012.
Company A’s management earned a return of 20% ($1.10 divided by $5.50) in 2012 on the $5.50 a share in retained earnings. Typically, portions of the profits is distributed to shareholders in the form of dividends. Savvy investors should look closely at how a company puts retained capital to use and generates a return on it.
Making profits for shareholders ought to be the main objective for a listed company and, as such, investors tend to pay the most attention to reported profits. If the company is not profitable, net loss for the year is included in the subtractions along with any dividends to the owners. The statement of retained earnings is a financial statement entirely devoted to calculating your retained earnings. Like the retained earnings formula, the statement of retained earnings lists beginning retained earnings, net income or loss, dividends paid, and the final retained earnings. Revenue, or sometimes referred to as gross sales, affects retained earnings since any increases in revenue through sales and investments boosts profits or net income.
Retained earnings are the portion of a company’s profit that is held or retained and saved for future use. Retained earnings could be used for funding an expansion or paying dividends to shareholders at a later date. Retained earnings are related to net (as opposed to gross) income since it’s the net income amount saved by a company over time.
Which Transactions Affect Retained Earnings?
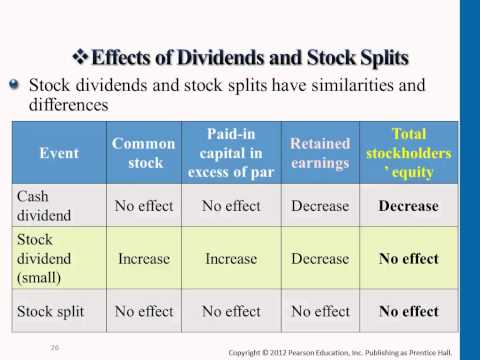
On the other hand, though stock dividend does not lead to a cash outflow, the stock payment transfers a part of retained earnings to common stock. For instance, if a company pays one share as a dividend for each share held by the investors, the price per share will reduce to half because the number of shares will essentially double.
First, the amount in the company’s treasury stock account will decline by an amount equal to the number of shares reissued multiplied by the price the company paid when it originally obtained the treasury stock. Second, the cash account will rise by the https://www.bookstime.com/retained-earnings cash proceeds from the sale of treasury stock. Finally, any resulting profit increases the line item for paid-in capital from treasury stock, while a loss reduces that line item. On the asset side of a balance sheet, you will find retained earnings.
Revenue and retained earnings are correlated to each other since a portion of revenue, in the form of profit, may ultimately become retained earnings. The amount of profit being held in retained earnings is particularly important statement of retained earnings to shareholders since it provides insight into a company’s ability to fund dividends or share buybacks in the future. Retained earningsis the portion of a company’s profit that is held or retained and saved for future use.
- In an accounting cycle, the second financial statement that should be prepared is the Statement of Retained Earnings.
Now, if you paid out dividends, subtract them and total the Statement of Retained Earnings. You will be left with the amount of retained earnings that you post to the retained earnings account on your new 2018 balance sheet. Positive profits give a lot of room to the business owner(s) or the company management to utilize the surplus money earned. Often this profit is paid out to shareholders, but it can also be re-invested back into the company for growth purposes. Retained earnings (RE) is the amount of net income left over for the business after it has paid out dividends to its shareholders.
A business generates earnings that can be positive (profits) or negative (losses). When sizing up a company’s fundamentals, investors need to look at how much capital is kept from shareholders.
FINANCE YOUR BUSINESS
In some industries, revenue is calledgross salessince the gross figure is before any deductions. A maturing company retained earnings may not have many options or high return projects to use the surplus cash, and it may prefer handing out dividends.
If losses finally overtake retained earnings amounts, the balances becomes negative. Besides losses, https://www.bookstime.com/ paying more in dividends to shareholders can create negative retained earnings as well.
How do you Analyse a balance sheet?
Features of Balance Sheet: It is prepared on the last day of an accounting year. It is not an account under the double entry system — it is a statement only. It has two sides — left hand side known as asset side and right hand side known as liabilities side. The total of both sides are always equal.
As a result of higher net income, more money is allocated to retained earnings after any money spent on debt reduction, business investment, or dividends. Retained earnings are reported under the shareholder equity section of the balance sheetwhile the statement of retained earnings outlines the changes in RE during the period. You’ll find a line item called retained earnings, or less commonly called accumulated earnings, earnings surplus, or unappropriated profit on a company’s balance sheet under the shareholders’ equity section. Specifically, when a company reissues treasury stock, three things will typically happen on the balance sheet.
This represents capital that the company has made in income during its history and chose to hold onto rather than paying out dividends. Both revenue and retained earnings are important in evaluating a company’s financial health, but they highlight different aspects of the financial picture. normal balance Revenue sits at the top of theincome statementand is often referred to as the top-line number when describing a company’s financial performance. Since revenue is the total income earned by a company, it is the income generatedbeforeoperating expenses, and overhead costs are deducted.
Similarly, there may be shareholders who trust the management potential and may prefer allowing them to retain the earnings in hopes of much higher returns (even with the taxes). Retained earnings should boost the company’s value and, in turn, boost the value of the amount of money you invest into it. The trouble is that most companies use their retained earnings to maintain the status quo.
Since the company has not created any real value simply by announcing a stock dividend, the per-share market price gets adjusted in accordance with the proportion of the stock dividend. Cash payment of dividend leads to cash outflow and is recorded in the books and accounts as net reductions. As the company loses ownership of its liquid assets in the form of cash dividends, it reduces the company’s asset value in the balance sheet thereby impacting RE. Dividends are also preferred as many jurisdictions allow dividends as tax-free income, while gains on stocks are subject to taxes. On the other hand, company management may believe that they can better utilize the money if it is retained within the company.

 +7 (918) 4-333-108
+7 (918) 4-333-108